Haven is a multi-agent hospital command center designed to augment clinical staff by creating a cohesive intelligence layer that automates monitoring, streamlines communication, and provides instant access to critical patient information.
The Problem
Hospitals are drowning in data, yet nurses spend up to 50% of their time on documentation instead of direct patient care. Information is fragmented across disconnected systems, leading to delays and communication gaps. This was inspired by a personal experience where a family member, hospitalized and needing assistance, often faced long waits for a nurse who then had to piece together information from multiple sources before they could help. The data was available, but it wasn't accessible when and where it was needed most. We envisioned a system where intelligent agents could act as the hospital's central nervous system, flagging critical patterns and preparing context-rich summaries for clinical staff instantly.
Tech Stack
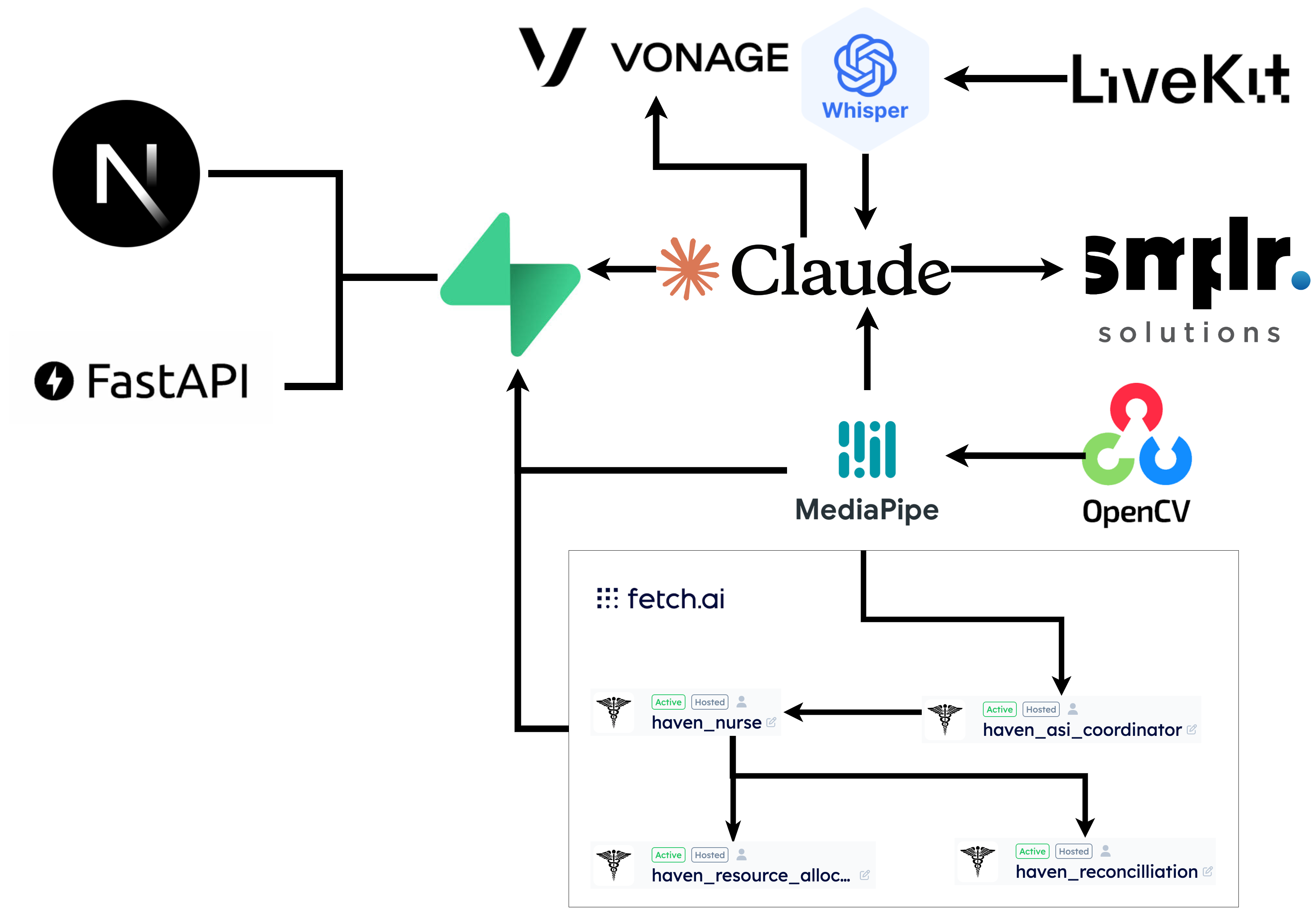
What Haven Does
Haven is an AI-powered coordination platform that provides three integrated layers of intelligence:
- Intelligent Voice Intake: Patients communicate naturally with a voice agent that asks structured follow-up questions, accesses validated EHR data, and generates concise, nurse-ready summaries and action items.
- Autonomous Monitoring: A coordinated network of Fetch.ai agents continuously analyzes patient status using a computer-vision pipeline built with OpenCV pose-estimation and a custom remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) model. The system adapts thresholds dynamically to balance false positives and reliably detect early clinical deterioration, triggering intelligent alerts before issues escalate.
- Spatial Intelligence Hub: A live 3D hospital map, powered by a Claude agent, provides a real-time spatial overview of the entire floor. Nurses can use natural language to query patient status, manage resources, and visualize alerts.
How It Works: A Multi-Agent Architecture
Haven's core strength lies in its distributed network of specialized agents that collaborate in real-time. Instead of a monolithic system, we designed a modular architecture where each agent handles a specific, high-stakes task.
Voice & Conversation Intelligence
The patient-facing voice agent is built on a high-speed, real-time pipeline.
- Real-time Interaction: We use LiveKit for robust WebRTC audio streaming, OpenAI Whisper for transcription, and Groq's LPU for near-instant LLM responses, creating a fluid, duplex conversation. Speech is synthesized using OpenAI TTS with the Nova voice.
- Precise Turn-Taking: The pipeline uses Silero VAD for voice activity detection, allowing the agent to distinguish between meaningful speech and pauses, ensuring it doesn't interrupt the patient.
- Intelligent Summarization: To manage context in long conversations, we built a summarization pipeline that compresses transcripts while preserving critical clinical details like pain levels, symptom descriptions, and emotional state, ensuring efficient context for both LLM interactions and nurse handoffs.
Autonomous Patient Monitoring & Vision
Patient vitals are tracked by a decentralized network of Fetch.ai agents and a novel computer vision pipeline.
- Agent Coordination: A dedicated agent monitors incoming data streams. When it detects an anomaly, it communicates with an an alerts agent, which cross-references the event with historical patient data to decide whether to raise or dismiss the alert.
- Non-Invasive Heart Rate Monitoring: We implemented a Facial Photoplethysmography (FPPG) pipeline using OpenCV. The algorithm identifies the patient's forehead as a region of interest (ROI), standardizes the RGB channels, and applies Fast Independent Component Analysis (FastICA) to the signal from an 8-second rolling window. This isolates the blood volume pulse from noise, allowing us to accurately extract the heart rate at approxmiately 30fps without physical sensors.
Spatial Command & Control
The 3D hospital map provides nurses with at-a-glance situational awareness.
- Natural Language Control: The map is controlled by an Anthropic Claude agent with multi-tool calling capabilities. A nurse can ask, "Show me which rooms have active alerts and summarize Dheeraj's questions from the last 6 hours."
- Autonomous Tool Execution: The agent autonomously executes the query by calling multiple tools: one to query the Fetch.ai network for active alerts and another to retrieve conversation summaries from the Supabase database.
- Real-Time Visualization: The map, rendered with Three.js, is updated instantly as the agent's tools return data. Room states are synchronized across all clients via Supabase WebSockets, ensuring the entire clinical team shares the same real-time view.
Challenges & Solutions
- Multi-Stream Synchronization: Coordinating concurrent WebSocket streams from LiveKit, Fetch.ai, and Claude while running the CV pipeline was a major challenge. We solved this by processing the computer vision pipeline in a background thread and implementing optimized synchronization protocols to maintain data consistency without blocking the UI.
- Natural Voice Interaction: Achieving a human-like conversation flow required extensive tuning of our voice activity detection parameters and building comprehensive exception handling to manage connection drops and overlapping speech.
- LLM Context Management: Long patient conversations quickly exceeded model context limits. Our solution was to develop an intelligent summarization pipeline that recursively compresses the conversation history, preserving only the most clinically relevant information.
Outcome
We successfully built a cohesive multi-agent ecosystem where AI agents from different providers (Fetch.ai, Claude, OpenAI) autonomously coordinate to deliver critical insights. The system demonstrates a powerful new paradigm for clinical decision support by integrating real-time voice interaction, non-invasive biometric monitoring, and spatial intelligence into a single, intuitive command center.
What’s Next
We plan to expand Haven's capabilities by introducing new specialized agents and enhancing its underlying technology.
Agent Ecosystem Expansion
- Medication Reconciliation Agent: Cross-references patient medications with new prescriptions to prevent dangerous interactions.
- Discharge Planning Agent: Coordinates with pharmacies, social workers, and home health services to streamline patient transitions.
- Resource Allocation Agent: Dynamically assigns rooms, equipment, and staff based on real-time hospital capacity and patient acuity.
Technical Enhancements
- Reinforcement Learning from Clinical Feedback (RLCF): Allow nurses to rate agent suggestions, enabling the system to learn hospital-specific workflows and improve its accuracy over time.
- Multi-modal Patient Monitoring: Integrate computer vision to detect fall risk, patient movement patterns, and other behavioral changes that complement vital sign monitoring.
- Federated Learning: Enable Haven deployments across different hospitals to learn from each other while maintaining strict patient privacy, creating a collective intelligence that improves with every installation.
Tagline
Haven: Your hospital's nervous system.
